| Home Page | Overview | Site Map | Index | Appendix | Illustration | Preface | Contact | Update | FAQ |
 |
 |
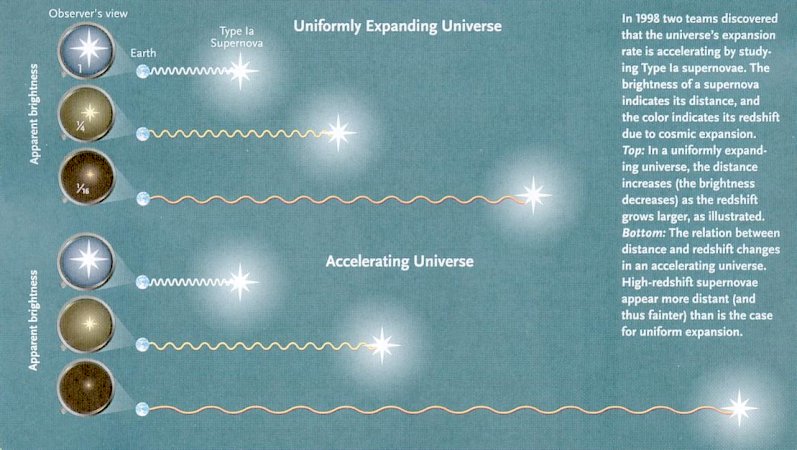
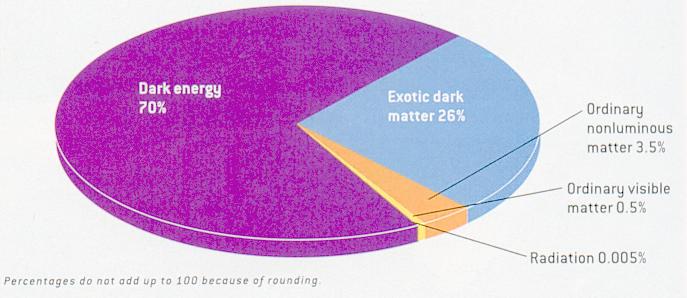
supernova appears to be dimmer than expected from an uniformly expanding universe. It is proposed that there is some kind of repulsive "dark energy" to induce the acceleration. Figure 02-10i shows the proportion of the various matter-energy components in the Universe. Most of the matter-energy content is in the form of "dark energy". The composition of the Universe is listed in Table 02-02 below. |
Figure 02-10h Supernova Ia |
Figure 02-10i Energy-Matter in the Universe |
New data in 2006 further refine the universe's contents to: 4% ordinary matter, 22% dark matter, and 74% dark energy. |
| Material | Representative Particles | Particle Mass or Energy (ev) | No. of Particles in Observed Universe | Probable Contribution to Mass of Universe | Sample Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary matter | Protons, electrons | 106 to 109 | 1078 | 5% | Direct observation, inference from element abundances |
| Radiation | photons | 10-4 | 1087 | 0.005% | Microwave telescope observations |
| Hot dark matter | Neutrinos | < 1 | 1087 | 0.3% | Neutrino measurements, cosmic structure |
| Cold dark matter | Supersymmetric particles? | 1011 | 1077 | 25% | Inference from galaxy dynamics |
| Dark energy | Scalar particles? | 10-33 | 10118 | 70% | Supernova observations of accellerated cosmic expansion |
Acceleration of the cosmic expansion is placed on a firmer footing when it is observed in 2003 that the CMBR becomes slightly hotter after going through a galaxy, which forms a gravitational (potential) well. Dark energy, being gravitationally repulsive, makes a gravitational well shallower as a photon passes through, so the photon exits with slightly more energy than it had when it entered.
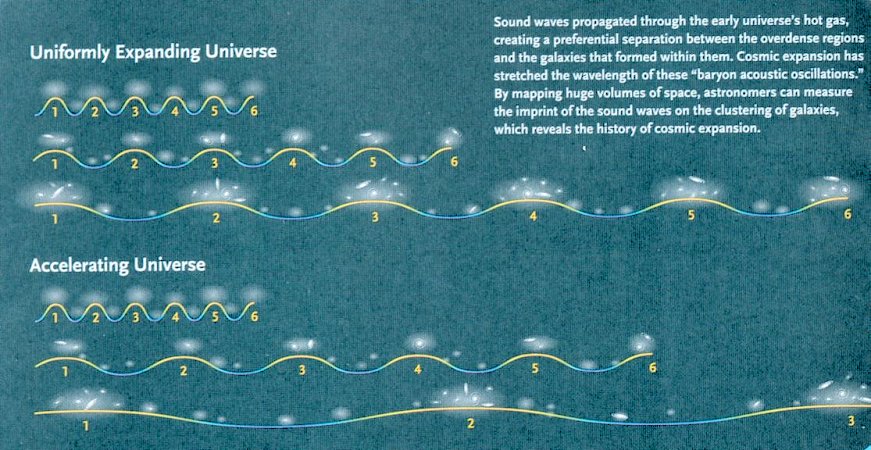 |
Another method to verify the cosmic acceleration is by detecting the bunching intervals of the clusters of galaxies. Whereas Type Ia supernovae behave like standard candles, the spacing between clusters of galaxies acts like a standard ruler. The bunching was generated by the cosmic sound wave, which compressed matter to higher density at its peaks. According to different scenarios of cosmic expansion, the amount of stretching is different as shown in Figure 02-10ja. In the primordial gas, the incoherent acoustic oscillations created peaks at intervals of 436000 light years, today the spacing should be about |
Figure 02-10ja Dark Energy and Sound Wave |
500 million light years depending on the kind of cosmic model (see Diagram b, Figure 02-10jb). |
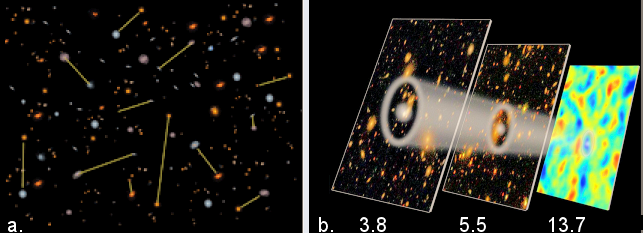 |
It was announced on March 30, 2012 that the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) has completed a massive survey of 327,349 galaxies out to about 6 billion light-years away. These galaxies are used as the standard rulers inside the clusters of galaxies to check out the cosmic acceleration. The survey confirms the 500 million light years "peak separation" at the present epoch, and estimates the transition to dark energy domination at 5 to 7 billion years ago (~ 9 - 7 |
Figure 02-10jb Cosmic Standard Ruler [view large image] |
Gyr since BB). Diagram a in Figure 02-10jb shows the various lengths of the cosmic rulers as defined by pairs of galaxies at different epoch (or redshift). Diagram b in the same figure illustrates the change in such length scale (represented by the white circle) over time (in unit of billion years ago). |
 |
 |
Gradually, it dawns on some astronomers that dark energy could be responsible for turning off galaxy and star formation in the latter half of the cosmic history at redshift z ~ 0.75 (~ 7.2 billion years since the Big Bang). The central piece of evidence is the rough coincidence in timing between the end of most galaxy and cluster formation and the onset of the domination of dark energy. Both happened when the universe was about half its present age. The influence of dark energy include stopping the merger of galaxies, sorting out the types of galaxies, lowering the rate of star formation, and preventing the growth of galaxy clusters (Figure |
Figure 02-10jc Dark Energy Evidences |
Figure 02-10k Galaxy Formation & Dark Energy |
02-10k). Such idea has been confirmed in 2008 by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The X-ray results on the hot gas in dozens of galaxy clusters some of which are relatively close and others are more than halfway across the universe reveal that accelerated expansion stifles the growth of |
 |
|
Figure 02-10l Dark Energy & Fates of the Universe [view large image] |
 |
|
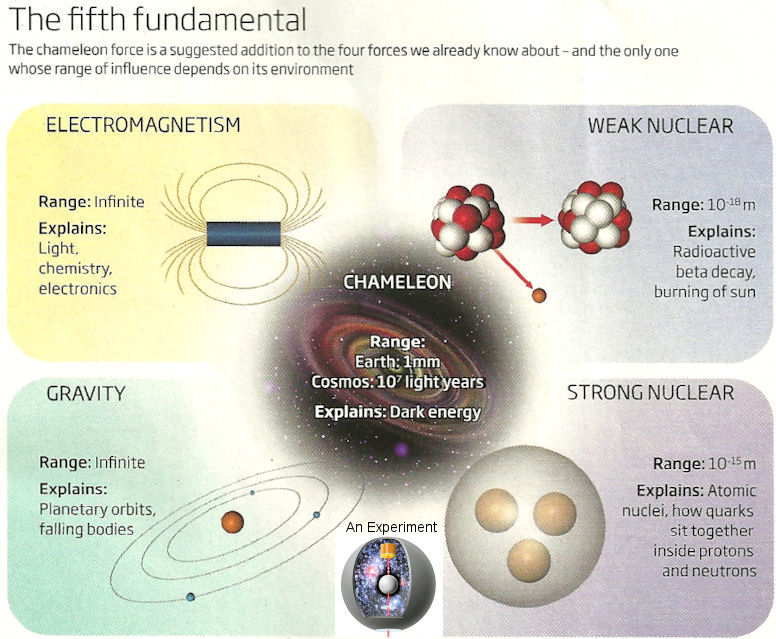
Figure 02-10m Chameleon Theory [view large image] |
 |
|
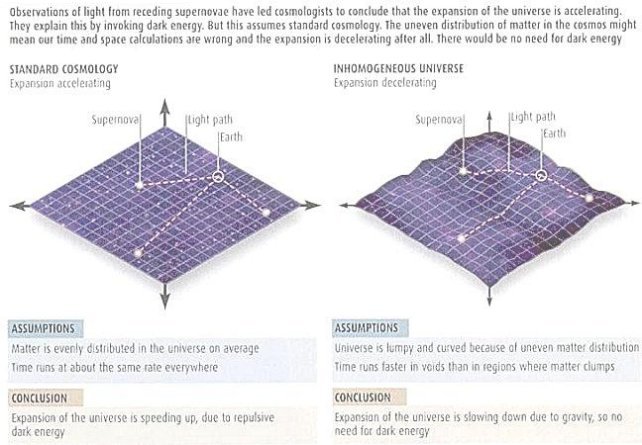
Figure 02-10n Dark Energy Illusion |
real. Since the CMBR photons gained a small amount of additional energy as they re-emerge from a gravitational well while the cosmic expansion is accelerating. |
 |
|
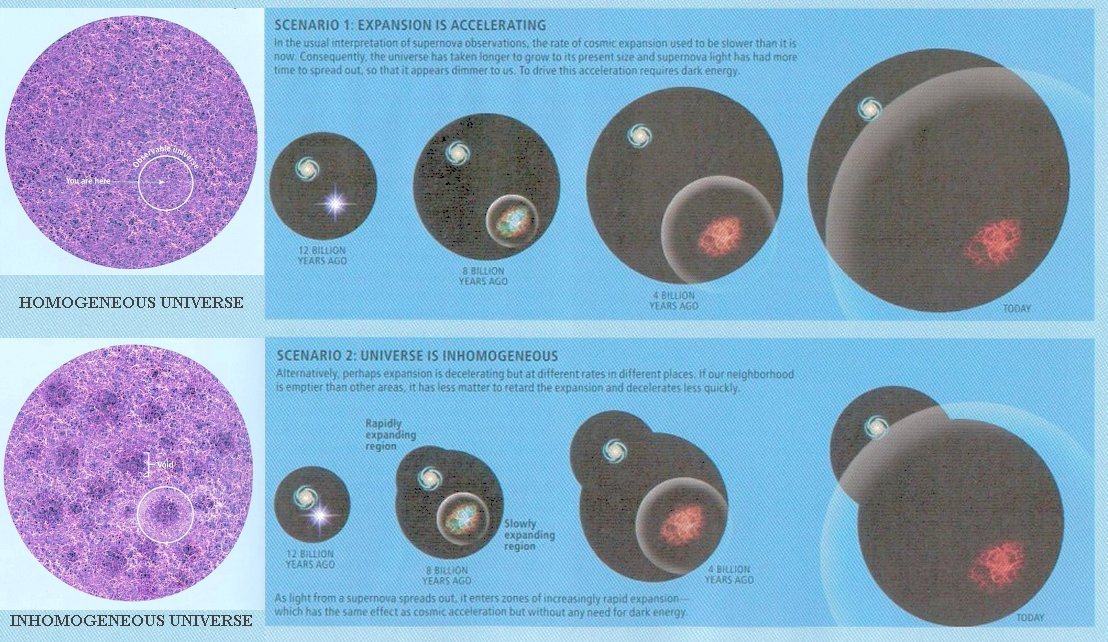
Figure 02-10o Earth in a Void [view large image] |
The observational sensitivity required to record the tiny changes is currently beyond astronomers' capabilities. But it should become feasible with a new generation of ultra-sensitive telescopes. |
 |
A preferred direction would also have other effects, such as large-scale coherent motions of galaxies and galaxy clusters. Several observations have claimed detection of such "dark flow", but it remains controversial. And then there is the argument that the "Void Theory" would not violate the Copernican principle (that the Earth is not special) if the region under consideration is very large and containing many more voids such as the inhomogeneous universe shown in Figure 02-10p, which also depicts the different explanations with dark energy and void. |
Figure 02-10p Inhomogeneous Universe [view large image] |
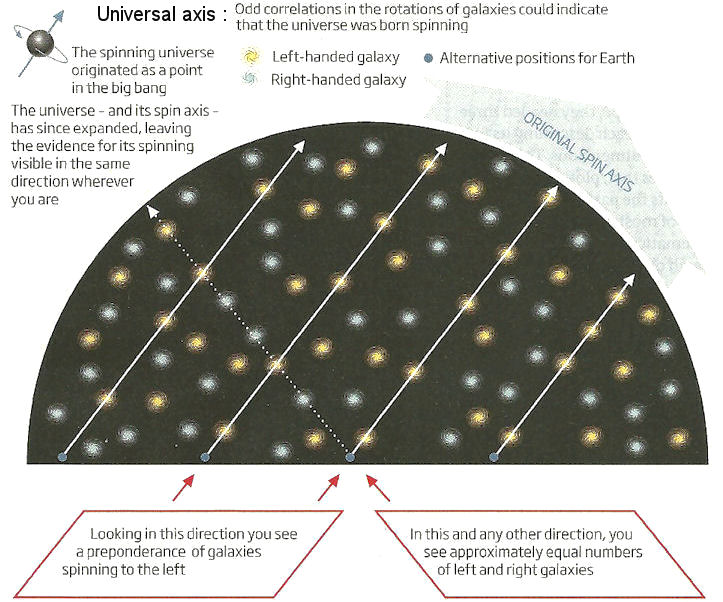 |
A 2011 study claims that along a direction at about 10 degree to the Milky-way's spinning axis there are more left-handed spirals (in the northern sky), while the opposite is observed in the southern sky. It is found that such axis is roughly in the same direction of the "axis of evil" mentioned above. The researchers claim that the universe was spinning at the the moment of Big Bang leaving some marks in the CMBR and the handedness of the spirals (Figure 02-10q). It is further speculated that an initially spinning universe brought on CP symmetry violation in gravity, which produced gravitational waves asymmetrically. Its interference with the inflaton field biased the production of matter over antimatter. This process left three marks behind : the axis of evil in CMBR, the inconspicuous alignment of the axes of rotating galaxies, and the all-matter universe. On top of all these speculations it is claimed lately in |
Figure 02-10q Spinning Universe [view large image] |
2011 that the cosmic expansion (in term of Type 1a Supernova observations) seems to go faster near the direction of the axis of evil. |
 |
|
Figure 02-10r2 Long EM Waves [view large image] |
 ) =
) =  8(
8( m/0.3)
m/0.3) ,
,  8 is the amplitude of matter fluctuations,
8 is the amplitude of matter fluctuations,  m the cosmic matter density parameter, and
m the cosmic matter density parameter, and  ~ 1/2. Thus, if
~ 1/2. Thus, if  8 = 0, the matter distribution would be smooth without any fluctuations.
8 = 0, the matter distribution would be smooth without any fluctuations.
 |
The Dark Energy Survey (DES) measured 300 million galaxies and their red shift to produce a 3-D map in a segment of 1/4 Southern Sky (Figure 02-10s,a). The number density neff together with gravitational lensing enable the determination of the fluctuation parameter  8 and the shear power S8 (Figure 02-10s,b). The result shows that the universe appears to be slightly smoother than the the value from CMB measurement by Planck, 2018. They also conclude that the dark energy density is constant over the eon. 8 and the shear power S8 (Figure 02-10s,b). The result shows that the universe appears to be slightly smoother than the the value from CMB measurement by Planck, 2018. They also conclude that the dark energy density is constant over the eon.
|
Figure 02-10s Dark Energy Survey [view large image] |
See "The most detailed 3D map of the Universe ever made" for more non-technical details. End of 2021 Update. |
 |
 |
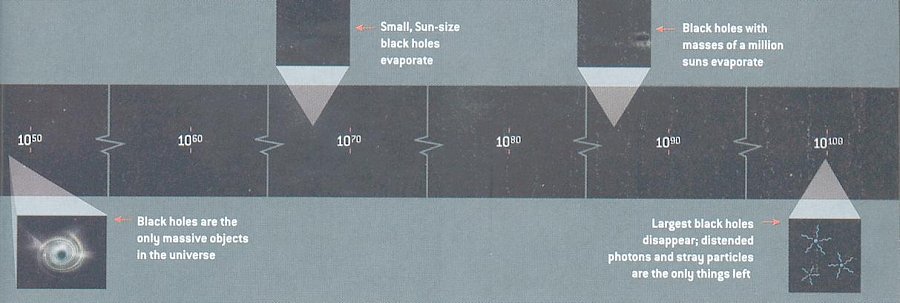 |
Figure 02-10t Future of the Universe |
 |
 |
local group of galaxies will collapse into a supergalaxy by gravitational attraction. Eventually, the universe goes black when the last stars burn out. Future civilizations (if there is any left) will have a very different perspective of the universe. Our descendants will observe an island of stars (the supergalaxy) embedded in a vast emptiness. It will resemble the de Sitter universe originally envisioned by Einstein. Figure 02-10u shows the sequence of events according to an artist's rendition. |
Figure 02-10u Future of the |
Milkyway [large image 1, 2] |
 |
Figure 02-10v shows the 2014 version of a "timeline of the universe" from a special issue of the "Astronomy" in September 2014. The timeline starts from 1000 years after the Big Bang (see the "Cosmic History Table" for textual explanation). This timeline contains more details on the epoch in which life is possible somewhere. Beyond the death of the Sun and the merge of the local group of galaxies about 100 billion years from now, the portray is mostly conjecture depending on the nature of dark energy which is still an enigma right now. |
Figure 02-10v Timeline of the Universe [view large image] |
 |
Since we don't feel the effect of dark energy and dark matter around us except through the gravitational influence on large scale, a model has been constructed with no other interactions between each other or with ordinary matter. It fits the observational data such as the high-redshift supernovae, the microwave background radiation, the distribution of large-scale structure, and the dynamic of celestial objects very well. But if 96% of the Universe is in the form of unseen substances, does this not mean that there is the possibility of hidden structure? Might the dark sector be a fascinating place, with its own intricate interactions - perhaps even a kind of intelligent life? Is there a 'dark light' that we do not see, radiating and absorbing in the dark Universe? Such possibility suggests that human beings are extremely unimportant |
Figure 02-10w Insignificance [view large image] |
in the grand scheme of the universe as portrayed in a 1985 movie called "Insignificance" in which Einstein and Monroe explore relativity and our place in the universe (Figure 02-10w). |
 ________________________________________
________________________________________