
| Home Page | Overview | Site Map | Index | Appendix | Illustration | About | Contact | Update | FAQ |
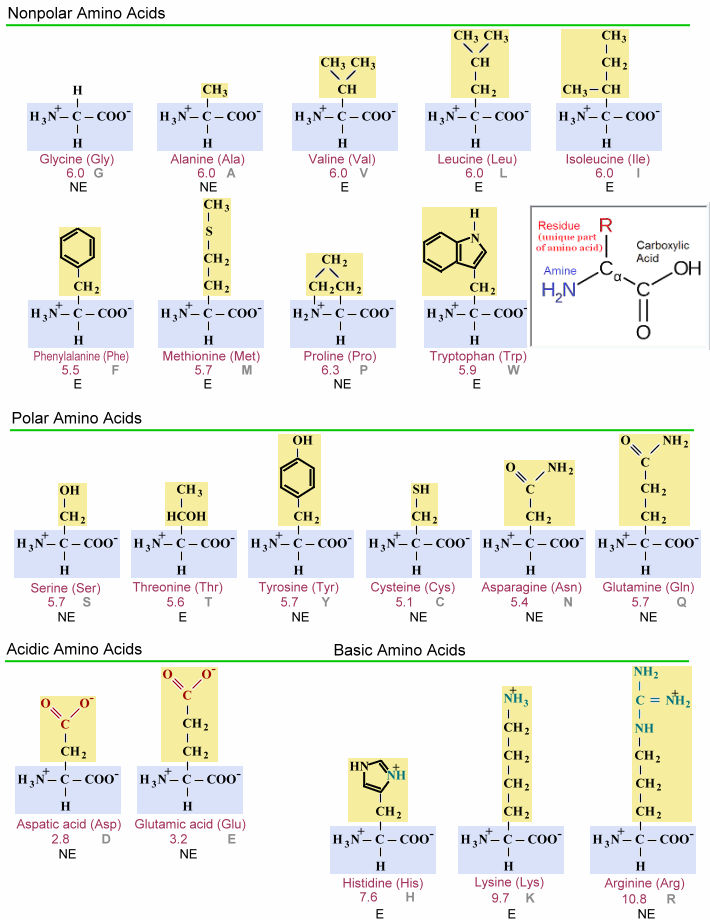 |
Figure 11-17 shows the 20 amino acids (with three-letters and one-letter abbreviations following the full name). Nonpolar amino acids are not soluble in water, which makes them hydrophobic. Polar amino acids have hydrophilic side chain, which forms hydrogen bonds3 with water. Acidic amino acids have side chains that can ionize as a weak acid. The side chains of the basic amino acids contain an amino group that can ionize as a weak base. The numbers at the bottom of each graph is the value of isoelectric point (pI). The isoelectric point is a value of pH at which the amino acid gives an overall charge of zero and not accepting or donating any H+ ion in a solution. The hexagon is the benzene ring C6H6. Amino acids on earth are all left-handed with the NH2 group to the left. Essential (E in Figure 11-17) amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be provided through diet, while non-essential (NE) amino acids are synthesized by the body from carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulphur. There are more amino acids beside those 20's used by biological system as listed in Figure 11-17. |
Figure 11-17 The 20 Amino Acids [view large image] |
 |
The bond that joins 2 amino acids is called a peptide bond. The NH2 and OH group at the end of the peptide are available for adding more amino acids to the chain. (Figure 11-18a). Combining amino acids to form peptide will release water, while adding water to peptide will break it up into individual amino acids. |
Figure 11-18a Peptide Formation [view large image] |
3The bonding energy for the various chemical bonds are roughly in the ratio - Van der Waals : Hydrogen Bonds : Covalent Bonds = 1 : 10 : 100. Formation of hydrogen bonds releases 3 - 10 kcal/mole (~ 0.1 - 0.4 ev). Hydrogen bonds are found between only a few elements of the periodic table. The most common are those in which H connects two atoms from the group F, O, N, and, less commonly, Cl. The hydrogen bond in water has the configuration: H-O-H(+)……..(-)O=H2. Covalent bonds are created with sharing electrons in between two atomic nuclei. A stable configuration can be achieved by sharing up to three pairs of electrons. Van der Waals forces are the intermolecular attractions produced by temporary dipoles (shifting of electrons).