|
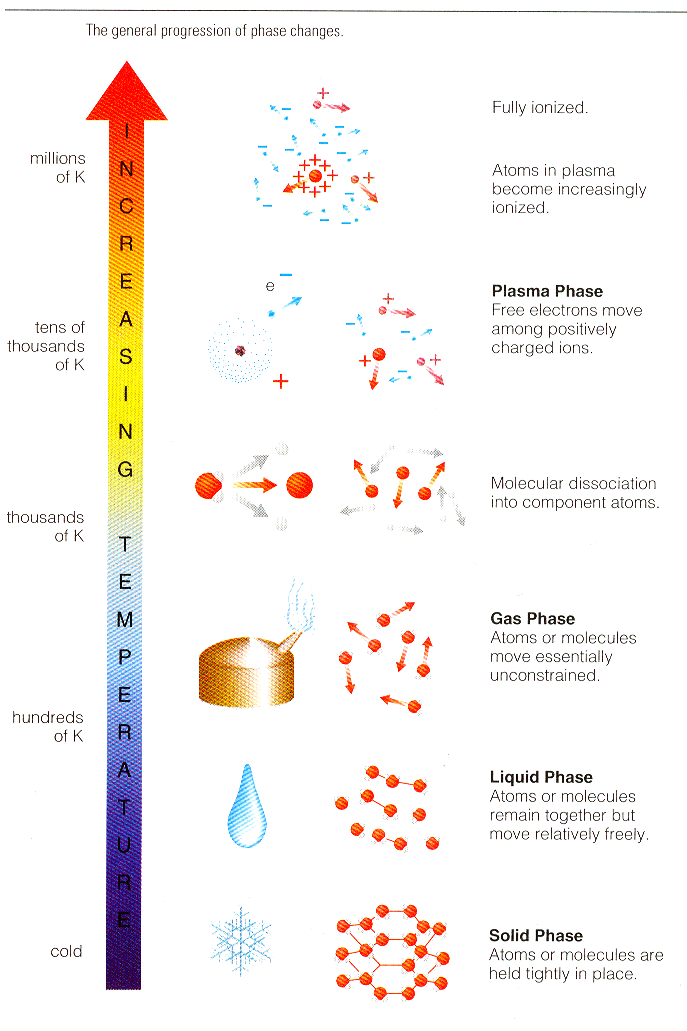
Depending on the temperature, the atoms may be partially or wholly ionized. A plasma may thus be considered as a mixture of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons, possibly co-existing with neutral atoms and molecules. For example, in our luminescent tube, the ions and electrons is a small proportion in relation to atoms and molecules. On the other hand, in plasmas produced for fusion experiments, the gas is strongly ionised, and the atoms and molecules are in low proportion, even completely absent in the heart of the pulse. In both cases, the description of plasmas comes from the physics of fluid mechanics and controlled by the force of electromagnetic interaction. The system is described by the usual macroscopic features such as density, temperature, pressure and rate of flow. |