| Complexity As |
Definition |
Example(s) |
Problem |
| Size |
Larger size means higher complexity |
Size of body or genome |
Some simple organisms have larger genome size than human's |
| SMI |
More variation signifies more complex message |
HHH... has no variation and zero entropy, the random sequence DXW... has lot of variation |
The most complex object is in between most orderly and complete randomness |
| Algorithmic Content |
Shorter computer program to describe the object corresponds to lesser complexity |
HHH... requires very short description, garbled message cannot be compressed |
Random object leads to high information content |
Logical
Depth |
Complexity is measured by how difficult to construct the object |
HHH... is very easy to construct, while a specific message requires more work |
It is difficult to measure the difficulty |
| Fractal Dimension |
Higher fractal dimension equals to higher complexity |
The coastal line is more complex than a straight line |
There are other kinds of complexity not defined by fractal dimension |
| Degree of Hierarchy |
Complexity is equated to the number of sub-systems |
Organ to cells to organelles to macro-molecules to ... |
It is difficult to separate the whole into parts |
 |
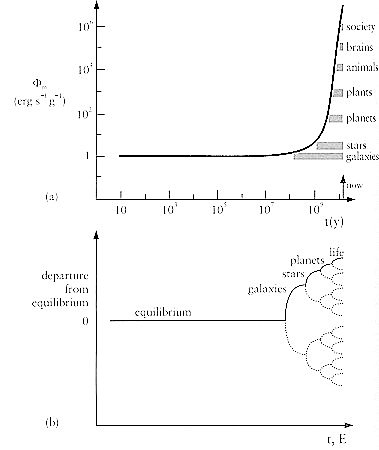
A working definition can be taken for ordinary discourse, which states: "it is a state of intricacy, complication, variety, or involvement, as in the interconnected parts of a structure - a quality of having many interacting, different components". Quantitatively, complexity can be measured roughly in term of the number of components such as the number of parts in a machine, the number of cell types in living organism (see Figure 11), or the vocabulary in a language. It is believed that complexity is created in nature by fluctuations - random deviations from some average, equilibrium value of density, temperature, pressure, etc. - also called "instabilities" or "inhomogeneities". Normally, an open system near equilibrium does not evolve spontaneously to new and interesting structures. It requires energy (~ force) to promote and maintain the off-equilibrium state.
|
Figure 11 Evolution to Greater Complexity [view large image] |
|