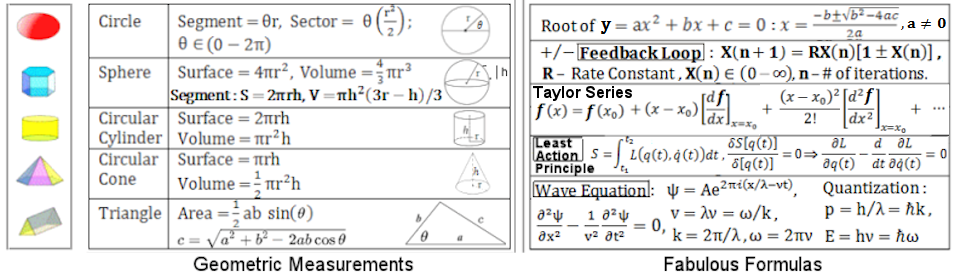
| Era |
Time
@ end of era |
Size (observable)
@ end of era |
Energy/Temp
@ end of era |
Relics & Observables |
Events (as re-constructed from theories) |
| Planck era |
< 5.4x10-44 sec |
< 1.6x10-33 cm |
> 1.2x1019 Gev |
(3+1)D space-time;
cosmic expansion |
Expansion started from a point to Planck scale; all forces united into one |
| GUT era |
<10-35 sec |
< 3x10-25 cm |
> 1014 Gev |
High energy cosmic rays; fundamental interactions
|
Separation of spacetime and matter; separation of gravitational, strong, and electroweak forces |
| Inflation (Rate of Expansion >>> c) |
< 10-32 sec |
< 3x10-22 cm = observable size
< 100 cm (unobs.) |
> 1014 Gev |
Un-observable universe;
large scale structures |
Reheating; Unstable vacuum;
quantum fluctuations |
| Electro-weak era |
< 10-11 sec |
< 0.3 cm
(see size scale) |
> 300 Gev |
Radiation; excess of matter over antimatter; separation of force (bosons), and matter (fermions) fields |
Radiation released in reheating; baryon-antibaryon asymmetry; separation of weak and electromagnetic forces; origin of mass |
| Hadron era |
< 1 sec |
< 3x1010 cm |
> 1.7 Mev |
Formation of hadrons |
Axion as dark matter |
| Weak decoupling |
< 4 min |
< 7x1012 cm |
> 100 kev |
neutron/proton ratio fixed |
Neutrinos decouple |
| Nucleosynthesis |
< 1/2 hour |
< 5x1013 cm |
> 40 Kev |
Fraction of Light elements |
Nuclear reactions freeze out, stable nuclei form |
Radiation era  Matter era Matter era |
< 0.24 My |
< 2x1023 cm |
> 0.6 ev |
Mass density fluctuations |
Matter density finally exceeds radiation density |
Recombination
 |
< 0.3 My |
< 3x1023 cm
|
> 3000oK |
CMBR  |
e- and p+ recombine into H atoms,
universe became transparent to light |
Dark ages
 |
< 1 Gy |
< 1027 cm |
> 100oK |
21 cm radio emission,
First stars, heavy elements |
mass fluctuations grow, first small objects coalesce, reionization  |
| Galaxy formation |
< 2 Gy |
< 2x1027 cm |
> 70oK |
Stars, quasars, galaxies |
Collapse to galactic systems |
| Bright age of Galactic Clusters |
< 12 Gy |
< 1028 cm |
> 3oK |
Solar system; decline of stellar formation from peak |
dark energy became dominant;
formation of clusters of galaxies |
| Present era |
~ 13.7 Gy |
~ 1.3x1028 cm |
~ 2.73oK |
Supercluster  |
Large scale gravitational instability |
| Topic |
Size |
Mass/Energy |
First Appearance |
Force and Phenomena |
| Macro-world |
Observable Universe a  |
1.3x1028 cm.
(cosmic horizon) |
4x1022 Msun
(including dark energy, ordinary and dark matters) |
0 sec. |
Gravity + Unknown repulsive force; an expanding space in the last 13.7x109 yrs, containing all the mass/energy of this world |
Superclusters a  |
1026 cm. |
1016 Msun
| 11x109 yr. |
Gravity; largest scale of lumpiness |
Clusters of Galaxies a  |
1024 cm. |
1015 Msun
| 6x109 yr. |
Gravity; galaxies in orbit around each other + dark matter |
Galaxies a  |
1022 cm. |
1011 - 1014 Msun
| 7x108 yr. |
Gravity; aggregation of stars, gas, dust and dark matter |
Star Clusters a  |
1020 cm. |
102 - 106 Msun
| 5x108 yr. |
Gravity; group of stars originated in an interstellar cloud |
Planetary Systems a  |
1016 cm. |
0.1-100 Msun
| 1.8x108 yr. |
Gravity; system of non-luminous bodies as by-product in stellar formation |
Stars a  |
1011 cm. |
0.1-100 Msun
| 1.8x108 yr. |
Gravity; contracting lump of gas with luminosity maintained by nuclear burning |
Earth g  |
109 cm. |
6x1027 gm. |
9.5x109 yr. |
Gravity; a planet in the habitable zone of the Solar system |
Living-world |
Multicellular Organisms b  |
104 - 10-1 cm. |
107 - 10-3 gm. |
13.5x109 yr. |
Residual Electromagnetic force; organisms composed of multiple cells |
Unicellular Organisms b  |
10-1 - 10-4 cm. |
10-3 - 10-12 gm. |
10.5x109 yr. |
Residual Electromagnetic force; one cell living unit |
Micro-world |
Molecules c  |
10-5 - 10-8 cm. |
10 - 10-3 ev.
| 3.8x105 yr. |
Residual Electromagnetic force; structure formed by combination of atoms |
Atoms c  |
10-8 cm. |
10 ev.
| 3.8x105 yr. |
Electromagnetic force; system of electrons and nuclei |
Nuclei p  |
10-13 cm. |
109 ev.
| 1 sec. |
Residual strong force; system of neutrons and protons |
Elementary Particles p  |
10-16 cm. > |
10-3 - 1012 ev.
| < 10-32 sec. |
Weak, strong and electromagnetic forces; basic constituents of matter and force |
| Era |
Period (MYA) |
GEOLOGICAL EVENTS |
BIOLOGICAL EVENTS |
| |
|
PRE-CAMBRIAN ERA |
|
| HADEAN |
4800 - 4000 |
Formation of Earth, solidification of crust,
evidence of water, heavy bombardment. |
Prebiotic (see "A 2018 Update on the Theory of Prebiotic World"). |
| ARCHEAN |
4000 - 2500 |
Beginning of rock record, evidence of plate
tectonics, magnetic field generation. |
Protozoa (unicellular organism). |
| PROTEROZOIC |
2500 - 541 |
Free oxygen in the atmosphere, glaciation¶,
solidification of inner core. |
Metazoa (multicellular organism). |
| |
|
PALAEOZOIC ERA |
(Era of Ancient Life) |
| CAMBRIAN |
541 - 485.4 |
Deposition of Burgess Shale. |
Invertebrates (trilobites), corals,
sea life of many types proliferating. |
| ORDOVICIAN |
485.4 - 443.4 |
Sea covered most of the planet. |
Vertebrates, first fish, mass extinction§. |
| SILURIAN |
443.4 - 419.2 |
High sea level. |
Land plants, jawed fishes, ammonoids. |
| DEVONIAN |
419.2 - 358.9 |
Gondwana, Laurasia beginning to form Pangaea. |
Amphibians, forests, sharks. |
| CARBONIFEROUS |
358.9 - 298.9 |
Swamps and coal bearing rocks. |
Insects, ferns. |
| PERMIAN |
298.9 - 252.2 |
Formation of Pangaea (the super-continent),
desertification occurred. |
Reptiles, conifers. |
| |
|
MESOZOIC ERA |
(Era of Middle Life, Age of Reptiles) |
| TRIASSIC |
252.2 - 201.3 |
Five million years "Dead Zone" in the tropics after end-Permian mass extinction. |
First dinosaurs. |
| JURASSIC |
201.3 - 145.0 |
Oldest surviving ocean floor. |
Height of dinosaurs, early mammals and birds. |
| CRETACEOUS |
145.0 - 66.0 |
Oil and gas deposits, broke up of Pangaea,
global mountain building. |
End of the dinosaurs, first flowering plants. |
| |
|
CENOZOIC ERA |
(Era of Modern Life, Age of Mammals) |
| TERTIARY |
66.0 - 2.588 |
Himalayas and Alps folded. |
Evolutionary separation of apes and
monkeys, most mammals established. |
| QUATERNARY |
2.588 - present |
Last ice age. |
Modern man. |
| STRUCTURE |
DESCRIPTION |
FUNCTION |
PKC |
| STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS |
|
|
|
| Cytosketeton |
Network of protein filaments |
Structural support; cell movement |
No |
| Flagella(cilia, microvilli) |
Cellular extensions |
Motility or moving fluids over surfaces |
Yes |
| Centrioles |
Hollow microtubules |
Moving chromosomes during cell division |
No |
| ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Plasma membrane |
Lipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded |
Regulates what passes into and out of cell; cell-to-cell communication |
Yes |
| Endoplasmic reticulum |
Network of internal membranes; forms compartments and vesicles |
Rough type processes proteins for secretion and synthesizes phospholipids; smooth type synthesize fats and steroids |
No |
| Nucleus |
Structure bounded by double membrane; contains chromosomes |
Control center of cell; directs protein synthesis and cell reproduction |
No |
| Golgi complex |
Stacks of flattened vesicles |
Modifies and packages proteins for export from cell; forms secretory vesicles |
No |
| Lysosomes |
Vesicles derived from Golgi complex that contain hydrolytic digestive enzymes |
Digest worn-out mitochondria and cell debris; play role in cell death |
No |
| Autophagy |
Vesicles to collect debris within the cell |
Malfunction causes accumulation of cell damage leading to diseases and aging (see Malfunction of Autophagy) |
No |
| ENERGY-PRODUCTING ORGANELLES |
|
|
|
| Mitochondria |
Bacteria-like elements with inner membrane |
Battery of the cell by ATP synthesis; site of oxidative metabolism |
No |
| ORGANELLES OF GENE EXPRESSION |
|
|
|
| Chromosomes (during cell division) / Chromatins |
Long threads of DNA that form a complex with protein |
Contain hereditary information |
Yes |
| Nucleolus |
Site of rRNA synthesis |
Assembles ribosomes |
No |
| Ribosomes |
Small, complex assemblies of protein, often bound to ER |
Site of protein synthesis |
Yes |
| Organ System |
Functions |
Components |
| Circulatory |
Transports nutrients, gases (O2, CO2), hormones and wastes through the body |
Heart, blood vessels and blood |
| Digestive |
Breakdowns and absorbs nutrients for growth and maintenance |
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, small and large intestines |
Endocrine
(Hormonal) |
Relays chemical messages through the body for controlling physiological processes |
Hypothalamus, pineal, pituitary, thyroid, thymus, pancreas and adrenal glands |
| Excretory |
Filters out cellular wastes, toxins and excess water or nutrients from the circulatory system |
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, lungs, sweat pores, and intestine |
| Immune |
Destroys or removes invading microbes, viruses; the lymphatic system also removes fat, and excess fluids from the blood. Skin is the outermost defense against pathogens |
Spleen, thymus, bone marrow, lymph, lymph nodes and vessels, white blood cells, T- and B- cells, skin |
| Musculo-skeletal |
Supports and moves organism; also protects delicate internal organs and provides attachment sites for the organs. |
Skeletal and smooth muscles; bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments |
Nervous &
sensory |
Relays electrical signals, directs movement, controls physiological processes, and responses to environment |
Brain, nervous system, and the five senses |
| Reproductive |
manufactures cells for reproduction |
Female: ovaries, oviducts, uterus, vagina, and mammary glands;
male: testes, as deferens, seminal vesicles, penis, and prostate gland |
| Respiratory |
Provides gas exchange between the blood and the environment |
Nose, trachea, and lungs |









 = 1. Its use is supposed to simplify the notation of the formulas. The table below shows the various physical quantities in natural units in columns 4 (in [cm]) and 6 (in [erg]). The factor to convert the formula back to cgs units are shown in columns 3, and 5 for the natural unit of [cm] and [erg] respectively; while the corresponding numerical value in cgs is obtained by division (for example the natural unit of energy density is ergs4, which has a numerical value of 1/(c
= 1. Its use is supposed to simplify the notation of the formulas. The table below shows the various physical quantities in natural units in columns 4 (in [cm]) and 6 (in [erg]). The factor to convert the formula back to cgs units are shown in columns 3, and 5 for the natural unit of [cm] and [erg] respectively; while the corresponding numerical value in cgs is obtained by division (for example the natural unit of energy density is ergs4, which has a numerical value of 1/(c )3 = 3.7x1049 ergs/cm3).
)3 = 3.7x1049 ergs/cm3).
 )
)
 )
) )
) )
)


 )1/2
)1/2 )1/2
)1/2 /c4)
/c4) )]
)] )
) 3)]
3)] ~ 3x10-17 erg-cm is involved in many of the backward conversions to cgs units, since the unit of [erg]/c
~ 3x10-17 erg-cm is involved in many of the backward conversions to cgs units, since the unit of [erg]/c
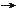 [cm-1]. This is closely related to the uncertainty principle : (
[cm-1]. This is closely related to the uncertainty principle : ( E)(c
E)(c t) = c
t) = c .
.

 Physical Constants
Physical Constants = 1/137
= 1/137  Fabulous Formulas
Fabulous Formulas