 |
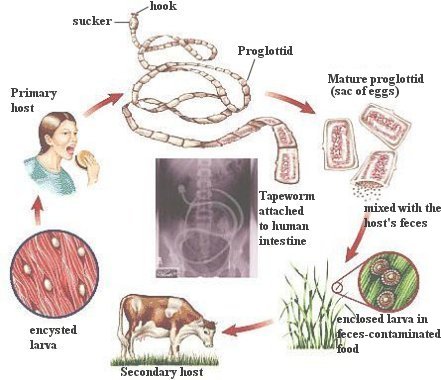
Flatworms are nonsegmented, lack a coelom, and have the sac body plan with only one opening. Therefore, if we analyze them according to Table 01, they have a combination of primitive and advanced features. There are three classes of flatworms: one is free living and two are parasitic. The free-living specimen, the planarian, best exemplifies the characteristics of the phylum. Tapeworms and flukes are parasitic with structure reflecting the modifications that occur in parasitic animals. Concomitant with the loss of predation, there is an absence of cephalization; the anterior end notably carries hooks and/or suckers for attachment to the host. The parasite acquires nutrient molecules from the host, and the digestive system is reduced. It is
|
|
covered by a specialized body wall resistant to host digestive juices. The extensive development of the reproductive system, with the production of millions of eggs, may be associated with difficulties in dispersing the species. Figure 06 shows the life cycle of the tapeworm. |


