
| Home Page | Overview | Site Map | Index | Appendix | Illustration | About | Contact | Update | FAQ |

|  |
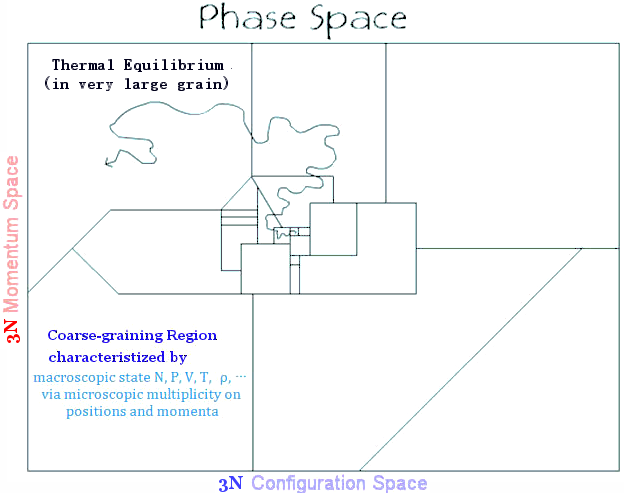
A general definition of entropy was formulated by Boltzmann in 1872. It is expressed in terms of "coarse-graining volume" in the phase space, which amalgamates the positions and momenta of all particles in a system into one point (Figure 01f). The relentless increase toward higher entropy until reaching its maximum (i.e., in a state of thermal equilibrium) is related to the fact that the evolution of the phase point is |
Figure 01f Phase Space [view large image] |
Figure 01g Phase Space Evolution |
more favorable toward the larger "coarse-graining volume" (Figure 01g). |
 E/E ~ 0.1). The size of the momentum space for each particle can be estimated from a range below and above the rms value such that about 0.1% probabilities toward the tail ends are excluded.
E/E ~ 0.1). The size of the momentum space for each particle can be estimated from a range below and above the rms value such that about 0.1% probabilities toward the tail ends are excluded. 3N/2(2mE)3N/2VN]/(N!)}(
3N/2(2mE)3N/2VN]/(N!)}( E/E), where
E/E), where p = (2mE)1/2(
p = (2mE)1/2( E/2E) is the range of momentum,
E/2E) is the range of momentum, 3N/2(2mE)(3N-1)/2 comes from integrating up to the energy E = p2/2m,
3N/2(2mE)(3N-1)/2 comes from integrating up to the energy E = p2/2m, E of the phase space. The Planck's constant h = 6.625x10-27 erg-sec from the uncertainty relation
E of the phase space. The Planck's constant h = 6.625x10-27 erg-sec from the uncertainty relation  p
p x ~ h in quantum theory is conveniently taken as the basic unit (minimum size) of the microscopic states. Thus the partition function Z is just:
x ~ h in quantum theory is conveniently taken as the basic unit (minimum size) of the microscopic states. Thus the partition function Z is just: 1/2(2mE)1/2V1/3)/h]3N/(N!)}(
1/2(2mE)1/2V1/3)/h]3N/(N!)}( E/E) ~ (10)2N(
E/E) ~ (10)2N( E/E)
E/E) E/E ~ 0.1).
E/E ~ 0.1).

| where k = 1.38x10-16 erg/oK is the Boltzmann constant. It is immediately clear that entropy would increase by adding # of particles N, energy E, or volume V as shown in Figure 01d (the internal degrees of freedom are not considered here). Since Z depends on the parameters in power of 3N, it varies by huge amount with a relatively small change in this parameter. |
Figure 01h Entropy and Randomness |
Figure 01h illustrates the connection of entropy with randomness once the support of orderliness is removed. |

|  |
properties such as temperature, pressure, density, color, chemical composition etc. which are some sort of averages out of a humonogous number of microscopic states - the multiplicity (see example in Figure 01j,  = Z) of positions and momenta. Its number of neighbors goes up drastically with increasing dimension, e.g., typically 6 in the 2 dimensional case, ~ 12 in 3 dimensions, ... according to = Z) of positions and momenta. Its number of neighbors goes up drastically with increasing dimension, e.g., typically 6 in the 2 dimensional case, ~ 12 in 3 dimensions, ... according to  (3N/2) in the formula above, the various w sub-volumes tend to differ in size by absolutely enormous factors. (3N/2) in the formula above, the various w sub-volumes tend to differ in size by absolutely enormous factors.
|
Figure 01i Coarse-graining Regions [view large image] |
Figure 01j Multiplicity |

| available for the same macroscopic state. The system reaches thermal equilibrium when the phase point enters the largest sub-volume and keeps wandering around inside (Figures 01h, 01i). Note that there is a certain probability of going into a smaller w, but the probability goes down rapidly with decreasing sub-volume size. |
Figure 01k Arrow of Time [view large image] |
|
|
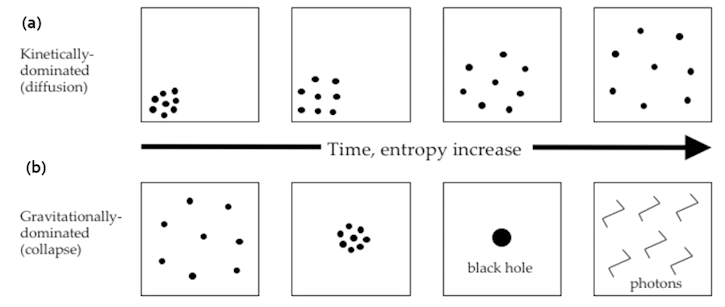
Figure 01l Entropy Evolution |
Figure 01l,a shows the evolution of entropy in free space with diffusion of particles. In Figure 01l,b the system is collapsing to black hole by the pull of gravity, the increase in entropy is via the Hawking radiation. Meanwhile the entropy of the black hole is reduced to at most three bits : |