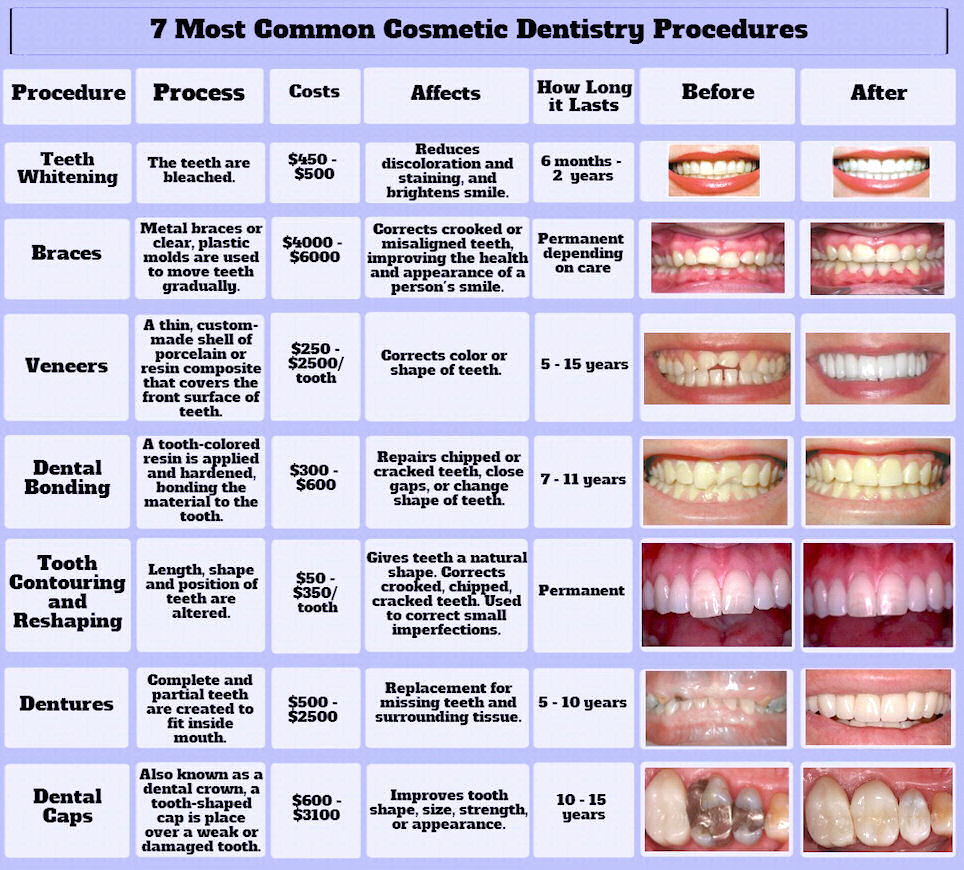
| Disease |
Symptom(s) |
Cause(s) |
Treatment(s) |
| Oral, Maxillofacial Pathology |
Dental caries (rotten teeth), damage to teeth supporting structures |
Congenital or acquired via fungus, bacteria, ... |
Dental restoration, tooth extraction
( see link) see link) |
| Oral Medicine |
Pain localized to the region above the neck, as well as pain within the oral cavity |
Afflicted by many gastrointestinal and cutaneous conditions |
Surgery ( see link) see link) |
| Orthodontics |
Dental irregularities : crowding, too much space, extra or missing teeth, cleft palate. |
Inherited, or acquired |
Correction by orthodontic braces
( see link) see link) |
| Periodontology |
Problems with supporting structures (periodontium) : gums, alveolar bone, cementum, and periodontal ligament |
Bacterial plaque in gums and teeth |
Removal of dental scale, bad fillings, crowns and other unwanted deposits, polishing tooth neck, etc. ( see link) see link) |
| Prosthodontics |
Lost Teeth |
Dental diseases, tooth developmental defects, genetic defects, trauma. |
Installing crowns, bridges, full or partial dentures, and dental implants ( see link) see link) |
| Root Canal Pain |
Toothache, sensitivity (to heat or cold), discoloration, swelling gum, pimple on gum |
Damaged pulp by infection |
Tooth is thoroughly cleaned then sealed
( see link) see link) |


 see link)
see link)