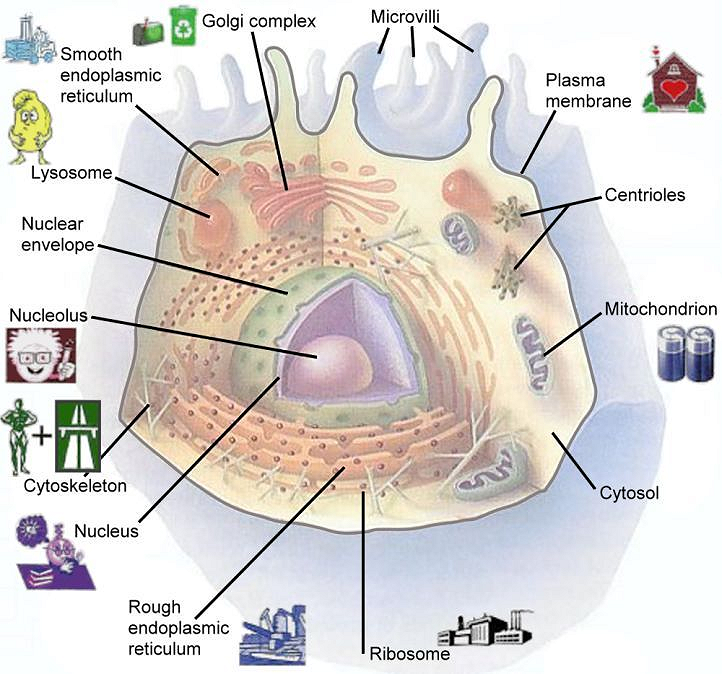
| STRUCTURE |
DESCRIPTION |
FUNCTION |
PKC |
| STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS |
|
|
|
| Cytosketeton |
Network of protein filaments |
Structural support; cell movement |
No |
| Flagella(cilia, microvilli) |
Cellular extensions |
Motility or moving fluids over surfaces |
Yes |
| Centrioles |
Hollow microtubules |
Moving chromosomes during cell division |
No |
| ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Plasma membrane |
Lipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded |
Regulates what passes into and out of cell; cell-to-cell communication |
Yes |
| Endoplasmic reticulum |
Network of internal membranes; forms compartments and vesicles |
Rough type processes proteins for secretion and synthesizes phospholipids; smooth type synthesize fats and steroids |
No |
| Nucleus |
Structure bounded by double membrane; contains chromosomes |
Control center of cell; directs protein synthesis and cell reproduction |
No |
| Golgi complex |
Stacks of flattened vesicles |
Modifies and packages proteins for export from cell; forms secretory vesicles |
No |
| Lysosomes |
Vesicles derived from Golgi complex that contain hydrolytic digestive enzymes |
Digest worn-out mitochondria and cell debris; play role in cell death |
No |
| Autophagy |
Vesicles to collect debris within the cell |
Malfunction causes accumulation of cell damage leading to diseases and aging (see Malfunction of Autophagy) |
No |
| ENERGY-PRODUCTING ORGANELLES |
|
|
|
| Mitochondria |
Bacteria-like elements with inner membrane |
Battery of the cell by ATP synthesis; site of oxidative metabolism |
No |
| ORGANELLES OF GENE EXPRESSION |
|
|
|
| Chromosomes (during cell division) / Chromatins |
Long threads of DNA that form a complex with protein |
Contain hereditary information |
Yes |
| Nucleolus |
Site of rRNA synthesis |
Assembles ribosomes |
No |
| Ribosomes |
Small, complex assemblies of protein, often bound to ER |
Site of protein synthesis |
Yes |