
| Home Page | Overview | Site Map | Index | Appendix | Illustration | About | Contact | Update | FAQ |

 |
 |
 |
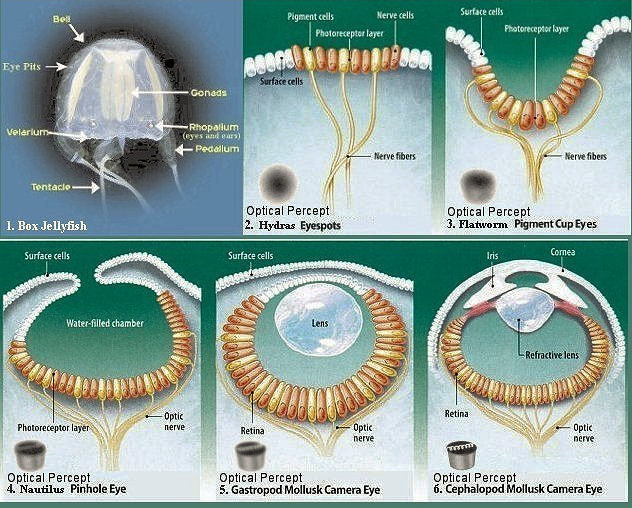
The first light-sensitive cells appeared in Cnidarians animals such as the hydras. Figure 24a illustrates the sequence of vision evolution with an insert to indicate the kind of light perception, and a short description for each step below. |
Figure 24a Evolution of Vision [view large image] |
Figure 24b Compound Eye |
Figure 25 Ophthalmology and Eye Anatomy |
| Disease | Symptom(s) | Cause(s) | Treatment(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cataracts | Cloudy, blurry, foggy, or filmy vision, color change, uncomfortable with glare, double vision, sudden changes in glasses prescription | Cloudy lens due to aging, drug, trauma, radiation, genetics, skin diseases, diabetes | Eye glasses change, surgery (  see link) see link) |
| Color Blindness | Trouble seeing red, green, or blue or a mix of these colors | Retinal cones deficiency by genetic, aging, injury, eye diseases, medicine | No cure, try specialized eye glasses to minimize impact ( see link) see link) |
| Corneal Diseases | Blurred vision, light sensitivity, pain | Inflections, trauma, genetic, autoimmune, nutrition deficiencies, allergies | Medications, laser treatment, surgery (  see link) see link) |
| Glaucoma | Dark rooms adjustment or focusing problem, sensitivity to glare, color of iris change, recurrent pain around eyes, double vision, distorted lines, tearing or "watery eyes", itching eyes, seeing things | Aging, eye pressure, inherited, nearsightedness, injuries, severe anemia, diabetes | Medicines, surgery (  see link) see link) |
| Macular Degeneration | Dark, blurry areas in the center of vision, diminished or changed color perception | Deterioration of the central portion of the retina (macula) | Drug, vitamins, therapy, vision aids ( see link) see link) |
| Myopia/Hyperopia | Blurry vision | Inherited, improper viewing, not enough day light for development | Eye glasses ( see link) see link) |
| Uveitis | Eye redness, blurred vision, eye pain, sensitivity to light, spots before the eyes | Infection with virus, fungus, bacteria, parasite, eye injury | Antibiotics, drug (  see link) see link) |
 |
 |
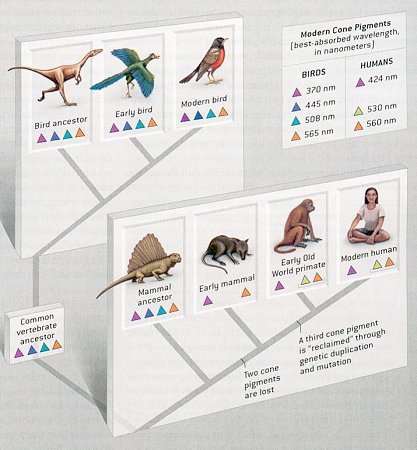
nocturnal and cones are not needed for vision in dim light. After the dinosaurs died out, mammals began to diversify, and the lineage that gave rise to the Old World primates of today reclaimed a third cone through duplication and subsequent mutation of the gene for one of the remaining pigments. Thus, mammalian colour vision distinctly limited when compared with the visual world of birds and other vertebrates especially in the near ultraviolet region of the spectrum. We cannot comprehend the sensation of colour in these animals, but a camera equipped to detect only ultraviolet light "sees" patterns invisible to us as shown in Figure 26b. |
Figure 26a Colour Vision |
Figure 26b UV Photo |

 (click me) to experience the perspective of color challenged individuals. The "abnormal" view is created by removing the corresponding part of the optical spectrum while taking the photo image. It has nothing to do with the "Hard Problem in Consciousness".
(click me) to experience the perspective of color challenged individuals. The "abnormal" view is created by removing the corresponding part of the optical spectrum while taking the photo image. It has nothing to do with the "Hard Problem in Consciousness".