

| Home Page | Overview | Site Map | Index | Appendix | Illustration | About | Contact | Update | FAQ |
 |
 |
inflation era about 10-32 sec after the Big Hang, the inflaton field (not yet identified) decayed from false vacuum to true vacuum, all its energy was converted to the particles in this world. Somehow about 10-10 sec further, the Higgs field mutated into a metastable form. It soon decayed into the true vacuum providing a mechanism to endow mass to other particles. The Standard Model (SM) is a mathematical formalism (Figure 03hf) to describe the behavior of the elementary particles since such transformation. |
Figure 03hd Quantum Fields [view large image] |
Figure 03he Virtual Particles [view large image] |
Figure 03hg shows roughly the history of the Higgs plus some pertinent formulas and data. See also a Table of Cosmic History. |

 4 (see Figure 03hg). The energy density E before the symmetry breaking has a form similar to the Harmonic potential, which is adhered to by all the quantum fields at or near ground state.
4 (see Figure 03hg). The energy density E before the symmetry breaking has a form similar to the Harmonic potential, which is adhered to by all the quantum fields at or near ground state. 0 = 0 at the top is unstable and soon decayed to the true vacuum where
0 = 0 at the top is unstable and soon decayed to the true vacuum where  0 = |M|/(2
0 = |M|/(2 )1/2 is called VeV (Vacuum expectation Value). It is related to the background probability for the presence of the Higgs boson. The Higgs bosons carry no momentum, they are everywhere to interact with coupling strength proportional to the mass of the particle. It is depicted in Figure 03hg with a "X" to indicate such state, while the dotted line represents interaction with other particles. It is not interacting with photon so that the photon is massless. Interaction to slow down the speed of other particles is interpreted as mass (see cartoon below).
)1/2 is called VeV (Vacuum expectation Value). It is related to the background probability for the presence of the Higgs boson. The Higgs bosons carry no momentum, they are everywhere to interact with coupling strength proportional to the mass of the particle. It is depicted in Figure 03hg with a "X" to indicate such state, while the dotted line represents interaction with other particles. It is not interacting with photon so that the photon is massless. Interaction to slow down the speed of other particles is interpreted as mass (see cartoon below).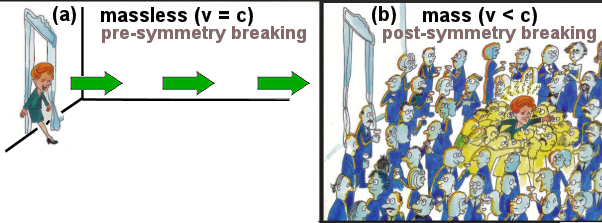
 3 (the Higgs sector in Figure 03hf). It is usually specified by the natural unit Gev4 = 2x1038 ergs/cm3 (in cgs).
3 (the Higgs sector in Figure 03hf). It is usually specified by the natural unit Gev4 = 2x1038 ergs/cm3 (in cgs).  |
 |
|
Figure 03hf WS in SM, Formulas [view large image] |
Figure 03hg Higgs History, Formulas, and Data [view large image] |
Figure 03hf shows the Lagrangian density of the Weinberg-Salam (WS) model (for electroweak interaction). |
 |
 0 = 0 at true vacuum, there is no probability for generating mass, i.e., no Yakawa and gauge couplings. The Higgs sector Lagrangian density in WS becomes 0 = 0 at true vacuum, there is no probability for generating mass, i.e., no Yakawa and gauge couplings. The Higgs sector Lagrangian density in WS becomes 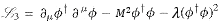 . .All the particles in this era are massless flying around at speed of light. There would be no chance for the formation of stars, galaxies, ... no structure at all. Figure 03hh shows the parameters for various elementary particles in the WS model just before and thereafter the transition. |
Figure 03hh WS in SM, Parameters [view large image] |
As shown in Figure 03hh, this is also the point when the electro-weak interaction separated into the weak (with massive mediating bosons - making the force short range) and electromagnetic (with the massless photon - producing long range force) interactions. |
 inverse of probing energy) and from small to large (see a few examples in Figure 03hi). Usually, the higher level does not involve the detail of the lower one, which just provides a few parameters as linkage between the two. These
inverse of probing energy) and from small to large (see a few examples in Figure 03hi). Usually, the higher level does not involve the detail of the lower one, which just provides a few parameters as linkage between the two. These
 |
 |
parameters summarize the more complicated details in just a few numerals, and often can be measured by experiment or observation. The high level description is often referred to as effective theory. For example in atomic physics, only the |
Figure 03hi Reductionist's Systems |
Figure 03hj QED Radiative Correction [view large image] |
mass and charge of the electron is necessary for such theory at 10 - 100 ev energy scale. |
 |
the electron getting closer because of the effect of vacuum polarization. Thus, QED is only valid in space beyond a radius of ~ 10-15 cm from the electron (~ 100 Gev, see Figure 03hk for the conversion). Figure 03hj,b shows the region dominated by the influence of the virtual particles. This single cutoff parameter defines the valid (energy / length) scale of the QED, beyond which a new theory, i.e., the SM would take over. |
Figure 03hk Energy Scale (molecules, atoms, nuclei are in binding energy) [view large image] |
Anyway, the QED self-energy correction for electron mass m = m0 +  m, where m is the observed mass, m0 the un-measurable bare mass covered by the virtual particles, and m, where m is the observed mass, m0 the un-measurable bare mass covered by the virtual particles, and  m = (3m m = (3m /2 /2 )loge( )loge( /m), /m),  = 1/137 is the fine structure constant for EM coupling. = 1/137 is the fine structure constant for EM coupling. |
 |
For the observed electron mass m = 0.5 Mev, and the cutoff at  = 100 Gev, we obtain = 100 Gev, we obtain  m ~ 0.01 Mev giving m0 ~ 0.49 Mev and m/m0 ~ 1.02. So everything appears to be normal, there is no fine-tuning. The novel feature of electro-weak unification in Standard Model beyond the cutoff would cover off the domain m ~ 0.01 Mev giving m0 ~ 0.49 Mev and m/m0 ~ 1.02. So everything appears to be normal, there is no fine-tuning. The novel feature of electro-weak unification in Standard Model beyond the cutoff would cover off the domain  100 Gev (see Figure 03hl, the GUT in which stands for "Grand Unified Theory" - a not yet verified theoretical model). 100 Gev (see Figure 03hl, the GUT in which stands for "Grand Unified Theory" - a not yet verified theoretical model).
|
Figure 03hl Coupling-Energy Curve |
 |
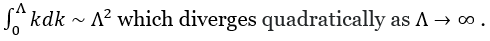 |
Figure 03hm Higgs Mass Radiative Corrections |
Figure 03hm lists some dominant corrections with a cutoff  = 10 Tev from which (m/ = 10 Tev from which (m/ m)2 ~ 0.024 for observed m = 125 Gev. It requires some fine tuning of m0 to arrive at such value of m (Figiure 03hm,b). m)2 ~ 0.024 for observed m = 125 Gev. It requires some fine tuning of m0 to arrive at such value of m (Figiure 03hm,b). |
 . It seems to be rather arbitrary in this example, because there is no theory of particle physics to explain such choice except those so-called "Theory Of Everything" (Figure 03hn) near the Planck scale of 1019 Gev from which yields a even more absurd ratio of (m/
. It seems to be rather arbitrary in this example, because there is no theory of particle physics to explain such choice except those so-called "Theory Of Everything" (Figure 03hn) near the Planck scale of 1019 Gev from which yields a even more absurd ratio of (m/ m)2 ~ 10-34 for m = 125 Gev. This is the "Hierarchy Problem" illustrated by a vast "Theory Desert" as shown in Figure 03hk.
m)2 ~ 10-34 for m = 125 Gev. This is the "Hierarchy Problem" illustrated by a vast "Theory Desert" as shown in Figure 03hk. |
 |
In summary, the "Hierarchy Problem with Higgs" is related to the fact that there is no theory in prospect near or beyond the 10 Tev scale to rationalize such choice of the cutoff, except some unproven hypotheses about quantum gravity |
Figure 03hn Theories of Everything |
Figure 03ho Defunct Solutions |
near "Planck Mass" level for which even more severe fine-tuning is required to produce the observed mass (see the absurdity of fine-tuning below). Figure 03ho shows some of the now defunct attempts to solve the hierarchy problem. |

 can be expressed as E =
can be expressed as E =  c/L, where L =
c/L, where L =  /2
/2 is the length scale of the matter wave. Therefore, the energy density (in cgs units) E/L3 =
is the length scale of the matter wave. Therefore, the energy density (in cgs units) E/L3 =  c/L4 = E4/(
c/L4 = E4/( c)3 or E4 = (
c)3 or E4 = ( c)3(E/L3). In natural unit c =
c)3(E/L3). In natural unit c =  = 1, then E4 = E/L3.
= 1, then E4 = E/L3. 